Vuex
Vuex 是专为 Vue 开发的状态管理库,可以解决组件间数据共享问题。
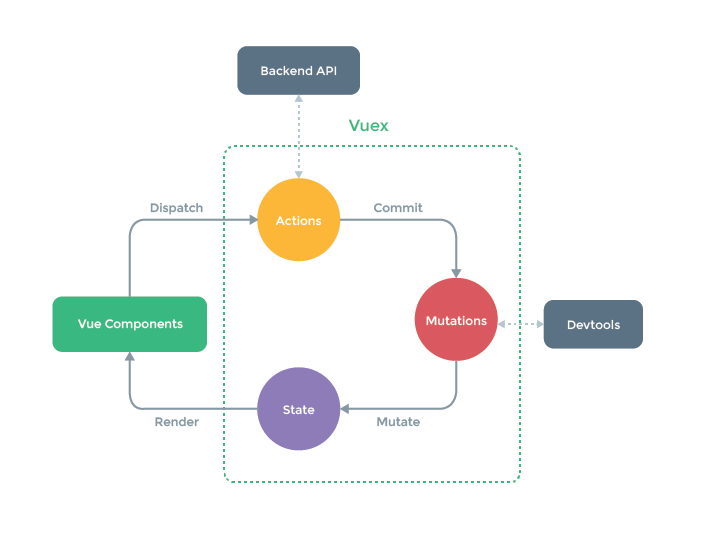
设计思想
借鉴 Flux 架构,应用的状态被集中存放在一个仓库中,仓库中的状态不能直接被更改,需要通过特定的方式来更新状态。
特性:
- 全局单例模式
- 单项数据流
核心概念
Vuex 中的五大核心概念:state、mutations、actions、getters、modules
mutation 处理同步的状态变更,action 处理异步的状态变更。
state
state 负责状态管理,用于管理当前应用状态。
单一状态树,每个应用只有一个 store 实例。
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
});
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
把 store 的实例注入到所有的子组件,可通过 this.$store 访问。
mutations
唯一可以更改 state 的方法,且是同步函数,通过 commit 触发。
- 接收两个参数:state、payload
- 事件类型一般习惯性全部大写,以下划线连接多个单词,如 SET_USERINFO
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
mutations: {
INCREMENT: (state, payload) => {
state.count += payload;
}
}
});
在组件中调用方式如下,这里的第二个参数就是 payload,可选参数。
this.$store.commit('INCREMENT', 123);
actions
可以处理异步,通过 dispatch 触发,不能直接修改 state。首先在组件中通过 dispatch 触发 action,然后在 action 函数内部 commit 触发 mutation,通过 mutation 修改 state 状态值。
action 函数接收一个 context 参数,该参数和 store 实例具有相同的方法和属性。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
INCREMENT: (state, payload) => {
state.count += payload;
}
},
actions: {
// incrementAsync(context, payload) {
// context.commit('INCREMENT', payload);
// },
// 使用解构简化
incrementAsync({ commit }, payload) {
commit('INCREMENT', payload);
}
}
});
调用方式:
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync', 123);
getters
getters 是 state 的计算属性,相当于 vue 中的 computed。依赖于 state 状态值,状态值一旦改变,getter 会重新计算。
接收两个参数:state、getters
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
userName: 'vuex'
},
getters: {
name: (state, getters) => state.userName
}
});
在组件中访问:this.$store.getters.name
modules
模块化分割,防止 state 过于庞大和冗余。
- 模块内部的 state 是局部的,外部必须通过模块名进行访问
- 模块内部的 getters、mutations、actions 默认是注册在全局命名空间的。通过
namespaced: true开启命名空间,使其成为带命名空间的模块。
辅助函数
state/getters/mutations/actions 这四个属性都能解构出来对应的方法:mapState、mapGetters、mapMutations、mapActions
解构到组件中的位置:
- 解构到 computed 中:mapState、mapGetters
- 解构到 methods 中:mapMutations、mapActions
mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: mapState({
count: state => state.count,
// 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
countAlias: 'count',
// 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
countPlusLocalState(state) {
return state.count + this.localCount;
}
})
};
当映射的计算属性的名称和 state 的节点名称相同时,可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
...mapState(['count'])
}
};
mapGetters
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['name', 'age'])
}
};
mapMutations
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations([
// 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
'increment'
]),
...mapMutations({
// 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
add: 'increment'
})
}
};
mapActions
import { mapActions } from 'vuex';
export default {
methods: {
...mapActions([
// 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
'increment'
]),
...mapActions({
// 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
add: 'increment'
})
}
};
目录组织形式
单独使用
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
userInfo: {}
},
mutations: {
SET_USERINFO(state, payload) {
state.userInfo = payload;
}
},
actions: {},
plugins: [
createPersistedState({
storage: {
getItem: key => sessionStorage.getItem(key),
setItem: (key, value) => sessionStorage.setItem(key, value),
removeItem: key => sessionStorage.removeItem(key)
}
})
]
});
export default store;
vuex 是将数据存储在内存中,刷新页面数据就丢失了。
vuex-persistedstate 插件是持久化 vuex 里的数据,防止页面刷新后丢失数据。
// 存储数据
this.$store.commit('SET_USERINFO', userinfo);
// 使用数据
this.$store.state.userInfo;
按属性拆分目录
目录结构:
-- store
-- index.js
-- state.js
-- getters.js
-- mutations.js
-- actions.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import { state } from './state';
import { getters } from './getters';
import { mutations } from './mutations';
import { actions } from './actions';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state, getters, mutations, actions });
export default store;
按功能模块拆分
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import modules from './modules';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules });
export default store;
modules文件夹下有index.js、account.js、setting.js等模块:
import account from './account';
import setting from './setting';
export default { account, setting };
export default {
namespaced: true, // 命名空间
state: {
user: undefined
},
getters: {
user: state => {
if (!state.user) {
try {
const user = localStorage.getItem(process.env.VUE_APP_USER_KEY);
state.user = JSON.parse(user);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
return state.user;
}
},
mutations: {
setUser(state, user) {
state.user = user;
localStorage.setItem(process.env.VUE_APP_USER_KEY, JSON.stringify(user));
}
}
};
在组件中使用:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
methods: {
// account表示模块命名空间,后面数组表示mutations里的方法
...mapMutations('account', ['setUser']),
init() {
this.setUser({ name: 'zgh', age: 23 });
// 或者使用如下的方式
this.$store.commit('account/setUser', { name: 'zgh', age: 23 });
}
}
};
监听变化
先在computed中拿到值,然后在watch中监听即可。
computed: {
refreshData() {
return this.$store.state.userName
}
},
watch: {
refreshData(v) {
if (v) {
// do something
}
}
}